
Wählen Sie eine
oder mehrere Sprachen aus
0,1,0
- Deutsch
- Englisch
- Chinesisch
- Spanisch
Laserbeschichten
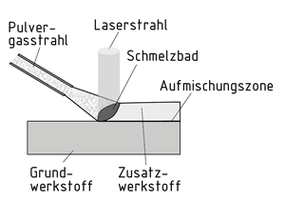
Das Laserbeschichten gehört zu den Fertigungsverfahren des Beschichtens. Mit Hilfe eines Lasers wird dabei eine festhaftende Schicht aus formlosem Stoff (Zusatzwerkstoff) auf die Oberfläche eines Werkstückes aufgebracht. Die Zusatzwerkstoffe können dabei in diversen Formen vorliegen, etwa als Pulver, Draht oder Paste.
Der Zusatzwerkstoff wird durch eine Vorrichtung zugeführt
Durch Laserbeschichtung können Oberflächen neu strukturiert oder repariert werden (Remanufacturing). Bei mehrschichtigem Auftrag eignet sich das Laserbeschichten zur Fertigung komplexer Werkstücke beim Rapid Prototyping und Rapid Tooling.
Laser coating
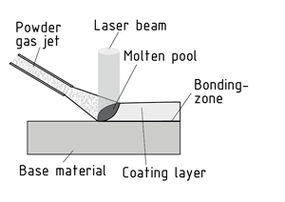
Laser Coating is a coating process. A laser is used to apply a firmly adhering layer of formless material (filler) to the surface of a workpiece. Fillers come in various forms, including powder, wire and paste.
A device supplies the filler material, which the laser beam then fuses with the surface of the base Material to form a coating layer. A diffusion zone is created between the base and filler materials during this process, which ensures a permanently and firmly bonded coating. In the case of metals, the process dissolves only a minimal amount of the base material, but produces a sealed metallurgical bond that exhibits excellent corrosion, abrasion and Wear Resistance.
Laser coating can be used to restructure or repair surfaces (remanufacturing) and multilayer laser coating to produce complex workpieces during Rapid prototyping and rapid tooling.
激光镀膜
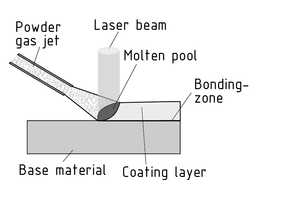
激光镀膜是一种。 使用将无定型材料(填料)牢固的粘附到工件的表面上形成镀层。填料有各种形状,包括粉末、线材和浆糊。
一台设备提供填充材料,在激光束的作用下和基体材料表面一起熔融以形成一层镀层。在此过程中,基层和填充材料之间形成扩散区,确保了永久牢固的胶粘镀层。若基层材料为金属,此工艺仅能溶解非常少的基体材料,但制造出无缝的冶金结合层且其具有出色的耐腐蚀性、耐磨耗性和耐磨损性。
激光镀膜可用于重组或修复表面(再制造)及多层激光镀膜,在快速原型和快速制模过程中生产复杂工件。
激光镀膜
近义词
激光沉积焊接
Recubrimiento láser
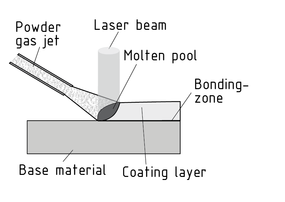
El recubrimiento láser es un . Un se usa para aplicar una capa firmemente adherente de material sin forma (relleno) en la superficie de una pieza de trabajo. Los rellenos vienen en diferentes formas, incluso polvo, alambre y pasta.
Un dispositivo suministra el material de relleno, el cual es fundido luego por el haz láser junto con la superficie del material base para formar una capa de recubrimiento. Se crea una zona difusa entre el material base y de relleno durante este proceso, la cual asegura un recubrimiento adherido de forma permanente y firme. En el caso de los metales, el proceso disuelve solo una cantidad mínima de material base, pero produce una unión metalúrgica sellada que presenta una excelente resistencia a la corrosión, abrasión y desgaste.
El recubrimiento láser se puede usar para reestructurar o reparar superficies (remanufacturar) y recubrimientos láser multicapa para producir piezas de trabajo complejas durante los prototipos rápidos y el mecanizado rápido.
Recubrimiento láser
