
Wählen Sie eine
oder mehrere Sprachen aus
0,1,0
- Deutsch
- Englisch
- Chinesisch
- Spanisch
Pascalsches Dreieck
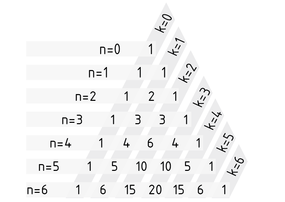
Das Pascalsche Dreieck ist ein Hilfsmittel zur Berechnung des Binomialkoeffizienten $\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)$(gelesen n über k). Es erlaubt auch einfache Berechnungen, etwa der Potenzen von Binomen. Die Binomialkoeffizienten sind im Pascalschen Dreieck so angeordnet, dass jeder Eintrag die Summe der zwei darüberstehenden Einträge darstellt. In der Gleichung, die dies darstellt, ist n der Zeilenindex und k der Spaltenindex:
$\left( \begin{matrix}n+1 \\k+1 \\\end{matrix} \right)=\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)+\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k+1 \\\end{matrix} \right)$.
Die Zählung beginnt bei $n=0$ und $k=0$. Sofern die ersten Randeinträge den Wert 1 haben, ergibt sich das Pascalsche Dreieck mit folgenden Binomialkoeffizienten:
Verallgemeinert kann gesagt werden, dass für ein beliebiges n im Pascalschen Dreieck in der n-ten Zeile am k-ten Platz der Binomialkoeffizient $\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)$ steht.
In der Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung werden wegen des hohen Rechenaufwandes Binomialkoeffizienten mit hohen n und k jedoch häufig als Näherungswert mit der Stirlingschen Formel bestimmt.
Pascal's triangle
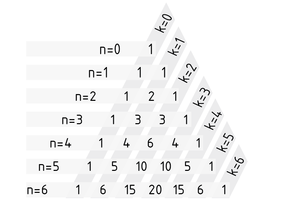
Pascal's triangle is used to calculate the binomial coefficient $\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)$(n over k) and for other simple calculations such as the powers of binomials. In Pascal's triangle, binomial coefficients are arranged in such a way that each entry represents the sum of the two entries above. In the relevant equation, n is the line index and k the column index:
$\left( \begin{matrix}n+1 \\k+1 \\\end{matrix} \right)=\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)+\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k+1 \\\end{matrix} \right)$.
Counting starts at $n=0$ and $k=0$. Initial entries of 1 at the edges produce a Pascal's triangle with the following binomial coefficients:
As a generalisation, the Binomial coefficient for any n in Pascal's triangle in position k on row n is $\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)$.
When calculating probabilities, however, binomial coefficients with high n and k values are often approximated using Stirling's formula because of the high complexity of the calculation that would otherwise be required.
杨辉三角
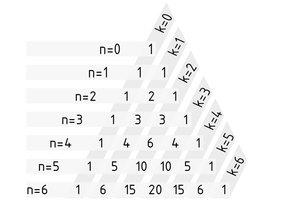
杨辉三角 用于计算 $\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)$ (从 n 个元素中 任取 k 个元素) 的二项式系数以及其他一些简单计算,比如,计算二项式的幂。在杨辉三角中,每个二项式系数都等于上一行两个数之和 。在有些方程中, n 表示行标,k 是列标:
$\left( \begin{matrix}n+1 \\k+1 \\\end{matrix} \right)=\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)+\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k+1 \\\end{matrix} \right)$。
从 $n=0$ 和 $k=0$ 开始进行计算。杨辉三角顶端的初始值为 1,生成下列二项式系数:
杨辉三角用于计算从n 个元素中任选 k个元素的二项式系数
总之,任意 n 值的二项式系数都在杨辉三角的第n 行第k 个位置上 $\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)$。
但是在计算概率时,由于n 和 k 的值都比较大,利用杨辉三角计算二项式系数非常复杂,因而通常用斯特林公式进行近似计算。
Triángulo de Pascal
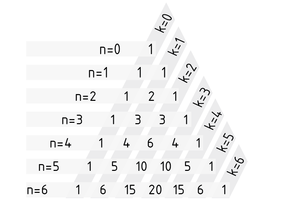
El triángulo de Pascal se usa para calcular el coeficiente del binomio $\left( \begin{matrix} n \\ k \\\end{matrix} \right)$ (n sobre k) y para otros cálculos simples como las potencias de los binomios. En el triángulo de Pascal, los coeficientes de los binomios se acomodan de manera tal que cada entrada representa la suma de las dos entradas anteriores. En la ecuación relevante, n es el índice de línea y k el índice de la columna:
$\left( \begin{matrix} n+1 \\ k+1 \\\end{matrix} \right)=\left( \begin{matrix} n \\ k \\\end{matrix} \right)+\left( \begin{matrix} n \\ k+1 \\\end{matrix} \right)$.
El conteo empieza en $n=0$ y $n=0$ . Las entradas iniciales de 1 en los extremos producen un triángulo de Pascal con los siguientes coeficientes de binomios:
El Triángulo de Pascal se usa para calcular el coeficiente del binomio para n sobre k
Como generalización, el coeficiente del binomio para cualquier n en el triángulo de Pascal en posición k en la fila n es de $\left( \begin{matrix} n \\ k \\\end{matrix} \right)$.
Sin embargo, cuando se calculan las probabilidades, los coeficientes de binomios con valores altos de n y k son a menudo aproximados usando la fórmula de Stirling, debido a la alta complejidad del cálculo que de otra manera sería requerido.
