
Choose one
or multiple languages
0,1,1
- German
- English
- Chinese
- Spanish
Binomial coefficient
The binomial coefficient $\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)$(n over k) is a mathematical function that can be used to determine the number of different ways in which k objects can be selected from a set of n different objects, ignoring the selection sequence.
$\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)=\frac{n!}{\left( n-k \right)!k!}$ where $n,k\in \mathbb{N}$ and $k\le n$
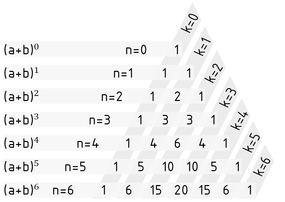
The binomial coefficient can be determined graphically using Pascal's triangle. This triangle also enables (straightforward) calculation of the coefficient with the help of recursion. The coefficients are arranged in the triangle in such a way that each entry represents the sum of the two entries above. However, the coefficients of ${{(a+b)}^{n-1}}$ need to be known to calculate the coefficients of ${{(a+b)}^{n}}$.
One application of the binomial coefficient is the binomial theorem:
${{(a+b)}^{n}}=\sum\limits_{k=0}^{n}{\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)\cdot {{a}^{k}}{{b}^{n-k}}}$ where $n,k\in \mathbb{N}$
The binomial coefficient is used for stochastic and analytical problems, for example to determine the binomial distribution. It is one of the most important functions of discrete probability distributions, for example in test series such as the Bernoulli process.
Binomialkoeffizient
Der Binomialkoeffizient $\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)$(gelesen n über k) ist eine mathematische Funktion, mit der festgestellt werden kann, auf wie viele verschiedene Arten man k Objekte aus einer Menge von n verschiedenen Objekten auswählen kann, ohne Berücksichtigung der Reihenfolge bei der Auswahl.
$\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)=\frac{n!}{\left( n-k \right)!k!}$ mit $n,k\in \mathbb{N}$ und $k\le n$
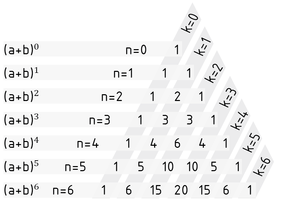
Im Pascalschen Dreieck kann der Binomialkoeffizient grafisch ermittelt werden. Es erlaubt mit Hilfe der Rekursion auch seine (einfache) Berechnung. Die Koeffizienten sind im Dreieck so angeordnet, dass jeder Eintrag die Summe der zwei darüberstehenden Einträge ist. Dabei müssen für die Berechnung der Koeffizienten von${{(a+b)}^{n}}$ jedoch die Koeffizienten von ${{(a+b)}^{n-1}}$ bekannt sein.
Eine Anwendung des Binomialkoeffizienten ist der Binomische Lehrsatz:
${{(a+b)}^{n}}=\sum\limits_{k=0}^{n}{\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)\cdot {{a}^{k}}{{b}^{n-k}}}$ mit $n,k\in \mathbb{N}$
Der Binomialkoeffizient wird für Fragestellungen in Stochastik und Analysis genutzt, etwa zur Feststellung der Binomialverteilung. Er ist eine der wichtigsten Funktionen der diskreten Wahrscheinlichkeitsverteilungen, etwa in Versuchsserien wie dem Bernoulli-Prozess.
二项式系数
二项式系数 $\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)$ (n 选 k)是一种数学函数,其用于确定从n 个不同物体中不计次序的任选k 个物体出来的各种组合数 。
$\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)=\frac{n!}{\left( n-k \right)!k!}$ 其中 $n,k\in \mathbb{N}$ 且 $k\le n$
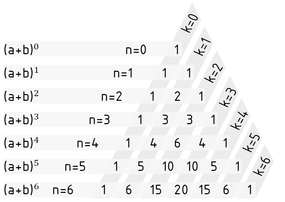
二项式系数可以用杨辉三角形象生动地计算出来。它是利用递推公式(直接)计算二项式系数。每个系数都是上一行两个数之和,所有系数都按照这种方式排列在三角形中。也就是说,为了计算 ${{(a+b)}^{n}}$ 的系数首先得知道 ${{(a+b)}^{n-1}}$ 的系数。
二项式系数的应用之一是二项式定理:
${{(a+b)}^{n}}=\sum\limits_{k=0}^{n}{\left( \begin{matrix}n \\k \\\end{matrix} \right)\cdot {{a}^{k}}{{b}^{n-k}}}$ 其中 $n,k\in \mathbb{N}$
利用杨辉三角计算二项式公式中的系数
二项式系数用于随机分析的问题,例如确定二项分布。二项分布是最重要的离散型概率分布,例如用于研究伯努利过程的试验序列。
Coeficiente del binomio
The binomial coefficient $\left( \begin{matrix} n \\ k \\\end{matrix} \right)$ (n sobre k) es una función matemática que puede ser usada para determinar el número de formas diferentes en las cuales los objetos k pueden ser seleccionados para una serie de objetos n diferentes, ignorando la secuencia de selección.
$\left( \begin{matrix} n \\ k \\\end{matrix} \right)=\frac{n!}{\left( n-k \right)!k!} $ donde $ n,k\in \mathbb{N} $ y $ k\le n$
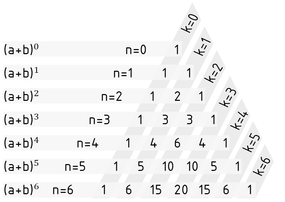
El coeficiente del binomio puede ser determinado gráficamente usando el triángulo de Pascal. Este triángulo también permite el cálculo (directo) del coeficiente con la ayuda de la recursión. Los coeficientes se acomodan en el triángulo de manera tal que cada entrada representa la suma de las dos entradas anteriores. Sin embargo, los coeficientes de ${{(a+b)}^{n-1}}$ deben conocerse para calcular los coeficientes de ${{(a+b)}^{n}}$ .
Una aplicación del coeficiente del binomio es el teorema binomial:
${{(a+b)}^{n}}=\sum\limits_{k=0}^{n}{\left( \begin{matrix} n \\ k \\\end{matrix} \right)\cdot {{a}^{k}}{{b}^{n-k}}} $ where $ n,k\in \mathbb{N} $
Triángulo de Pascal para calcular los coeficientes de las fórmulas de binomios
El coeficiente del binomio se usa para problemas estocásticos y analíticos, por ejemplo, para determinar la distribución binomial. Es una de las funciones más importantes de la distribución de probabilidad discreta, por ejemplo, en series de pruebas como el proceso de Bernoulli.
