
Choose one
or multiple languages
0,1,1
- German
- English
- Chinese
- Spanish
Diode
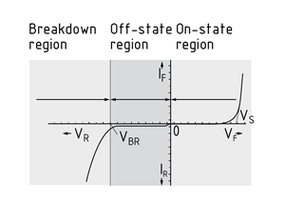
A diode is the most basic passive component in semi-Conductor technology. It is mainly used for uncontrolled Rectifier circuits.
Diodes are made up of one p-doped and one n-doped Semi-conductor. The free charge carriers balance each other out at the p-n junction formed. This creates the depletion or diffusion layer where the diffusion current flows. Applying an external voltage in the conducting direction - the diode works in the on-state region - reduces the potential barrier in the depletion layer and the diffusion current increases exponentially. Reversing the polarity of the voltage applied increases the potential barrier and the diffusion decreases exponentially. The diode is located in the off-state region. In the case of silicon diodes, the on-state voltage is $ \approx 0.6...0.7V$.
When designing diodes, care needs to be taken not to exceed the maximum off-state voltage ${V_{BR}}$, as this results in a breakdown and the associated destruction of the component (breakdown region).
