
Choose one
or multiple languages
0,1,1
- German
- English
- Chinese
- Spanish
GTO thyristor
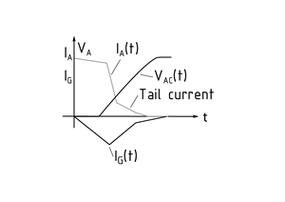
GTO (gate turn-off) thyristors are important components in Power electronics and drive technology when high switching capacities need to be achieved at frequencies of up to 1 kHz.
The special feature of GTO thyristors is that they can be switched off by a sufficiently high negative current thanks to the semi-Conductor chips' complex surface structure. To do so, the product of the turn-off amplification and the gate current ${I_G}$ must equal the flowing anode current ${I_A}$. Since the turn-off amplification lies between 2 and 2.5, the circuit must be designed for a very high negative gate current. This results in relatively complex wiring.
The tail current is a characteristic feature of the switching-off process with GTO thyristors. When this process starts, the voltage ${U_{AC}}$ increases. By the end of the process, the tail current tends towards zero. This essentially creates switching losses.
