
Choose one
or multiple languages
0,1,1
- German
- English
- Chinese
- Spanish
Integral calculus
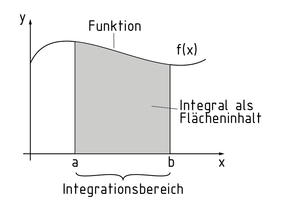
Integral calculus is used to determine the area S below a function $F(x)$ within the limits of integration $(a,b)$. The integral is worked out by subtracting the antiderivatives F at the upper limit from those at the lower limit. The function to be integrated $f(x)$ is called the integrand and x is the integration variable.
The formula \[\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)dx=F(b)-F(a)\,}\] applies and the integral is defined in this case.
If the limits of integration are not defined, the integral is an indefinite integral. It produces an antiderivative F(x) plus an integration constant C.
Relevant reference works contain antiderivatives for the most important functions alongside the integration rules.
Integralrechnung
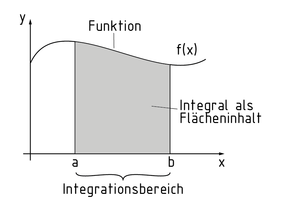
Bei der Integralrechnung wird die Fläche S unter einer Funktion $F(x)$ innerhalb der Integrationsgrenzen $(a,b)$ bestimmt. Das Integral ergibt sich durch Subtraktion der Stammfunktionen F an der oberen von der unteren Grenze. Die zu integrierende Funktion $f(x)$ heißt Integrand. Das x ist dabei die Integrationsvariable.
Es gilt: \[\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)dx=F(b)-F(a)\,}\]. Das Integral ist in diesem Fall bestimmt.
Sind die Integrationsgrenzen nicht gegeben, handelt es sich um ein unbestimmtes Integral. Dessen Ergebnis ist eine Stammfunktion F(x) plus einer Integrationskonstante C.
Die Stammfunktionen der wichtigsten Funktionen finden sich neben den Integrationsregeln in Nachschlagewerken.
积分
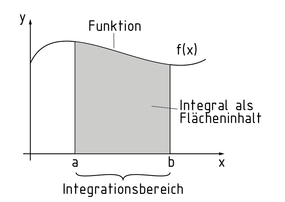
定积分用于求解在积分区域 $(a,b)$ 内部,函数 $F(x)$ 下方区域的面积 S。积分值是原函数F的积分上限与积分下限函数值之差。被求积分的函数 $f(x)$ 称为被积函数 ,x 为积分变量。
公式如下 $\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)dx=F(b)-F(a)\,}$ 利用该公式计算定积分。
如果积分没有上下限,这种积分为不定积分。不定积分得到的是函数的反导数(原函数) $F(x)$ 加上一个积分常数 C。
除了积分的基本公式,在参考书中提供一些重要函数的原函数的计算公式。
积分可以用来计算曲线下方曲边梯形的面积
近义词
反导数/原函数
被积函数
Cálculo integral
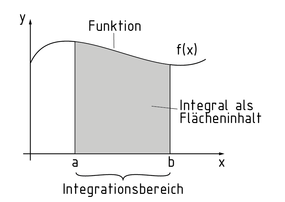
El cálculo integral se usa para determinar el área S debajo de una función $F(x)$ dentro de los límites de integración $(a,b)$ . La integral se resuelve al sustraer las antiderivadas F en el límite superior de las que se encuentran en el límite inferior. La función a ser integrada $f(x)$ se llama integrando y x es la variable de integración.
La fórmula $\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)dx=F(b)-F(a)\,}$ aplica y la integral es definida en este caso.
Si los límites de integración no son definidos, la integral es una integral indefinida. Produce una antiderivada F(x) más una constante de integración C.
Los trabajos de referencia relevantes contienen antiderivadas para las funciones más importantes junto con las reglas de integración.
Integral para determinar el área debajo de una curva
