
Seleccione uno
o más idiomas
0,1,3
- Alemán
- Inglés
- Chino
- Español
Esfuerzo alternante
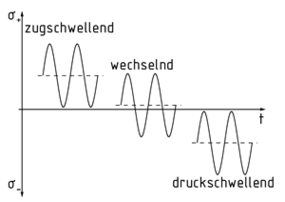
En el caso de un esfuerzo alternante, las fuerzas cíclicas actúan en un componente con un cambio de dirección. Esta es la situación cuando el esfuerzo máximo ${{\sigma }_{o}}$ está en la dirección opuesta al esfuerzo mínimo ${{\sigma }_{u}}$ .
Dividir el esfuerzo mínimo por el esfuerzo máximo da como resultado la relación de esfuerzos $R=\frac{{{\sigma }_{u}}}{{{\sigma }_{o}}}$ . El esfuerzo medio ${{\sigma }_{m}}$ es el esfuerzo promedio calculado usando los valores mínimos y máximos. Basado en esto, se distingue entre los siguientes escenarios:
${{\sigma }_{m}}<0 $ :
Si los esfuerzos máximos y mínimos son ambos negativos, el resultado es un esfuerzo de compresión pulsante.
Si el esfuerzo máximo es igual a cero y el esfuerzo mínimo es negativo, el resultado es un esfuerzo de compresión pulsante puro.
Si los esfuerzos mínimos y máximos actúan en direcciones opuestas y no son iguales, el resultado es un esfuerzo alternante.
${{\sigma }_{m}}=0$ : Esto indica un esfuerzo alternante puro.
${{\sigma }_{m}}>0$ :
Si los esfuerzos mínimos y máximos actúan en direcciones opuestas y no son iguales, el resultado es un esfuerzo alternante.
Si el esfuerzo mínimo es igual a cero y el esfuerzo máximo es positivo, el resultado es un esfuerzo de tensión pulsante puro.
Si los esfuerzos máximos y mínimos son ambos positivos, el resultado es un esfuerzo de tensión pulsante.
Perfil de esfuerzo para un esfuerzo alternante/pulsante
Wechselbeanspruchung
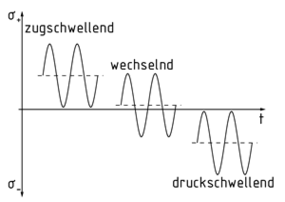
Bei der Wechselbeanspruchung wirken Kräfte zyklisch und mit einer Richtungsänderung auf ein Bauteil. Dies ist der Fall, wenn die größte auftretende Spannung, die sogenannte Oberspannung${{\sigma }_{o}}$, gegensätzlich zu der kleinsten auftretenden Spannung, der Unterspannung${{\sigma }_{u}}$, gerichtet ist.
Der Quotient aus Unter- und Oberspannung ergibt das sogenannte Spannungsverhältnis $R=\frac{{{\sigma }_{u}}}{{{\sigma }_{o}}}$. Die sogenannte Mittelspannung ${{\sigma }_{m}}$ist der Mittelwert aus Ober- und Unterspannung. Abhängig von dieser werden folgende Fälle unterschieden:
${{\sigma }_{m}}<0:$
- Sind Ober- und Unterspannung jeweils negativ, so liegt eine Druckschwellbeanspruchung vor.
- Ist die Oberspannung gleich null und die Unterspannung negativ, liegt eine reine Druckschwellbeanspruchung vor.
- Sind Ober- und Unterspannung gegensätzlich gerichtet und betragsmäßig ungleich, liegt eine Wechselbeanspruchung vor.
${{\sigma }_{m}}=0$: Es liegt eine reine Wechselbeanspruchung vor.
${{\sigma }_{m}}>0:$
- Sind Ober- und Unterspannung gegensätzlich gerichtet und betragsmäßig ungleich, so liegt eine Wechselbeanspruchung vor.
- Ist die Unterspannung gleich null und die Oberspannung positiv, liegt eine reine Zugschwellbeanspruchung vor.
- Sind Ober- und Unterspannung jeweils positiv, so liegt eine Zugschwellbeanspruchung vor.
Alternating stress
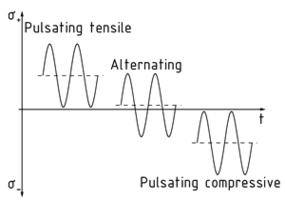
In the case of alternating stress, cyclic forces act on a component with a change of direction. This is the situation when the maximum stress${{\sigma }_{o}}$ is in the opposite direction to the minimum stress${{\sigma }_{u}}$.
Dividing the minimum stress by the maximum stress gives the stress ratio $R=\frac{{{\sigma }_{u}}}{{{\sigma }_{o}}}$. The mean stress ${{\sigma }_{m}}$is the average stress calculated using the maximum and minimum values. Based on this, a distinction is made between the following scenarios:
${{\sigma }_{m}}<0:$
- If the maximum and minimum stresses are both negative, the result is a pulsating compressive stress.
- If the maximum stress equals zero and the minimum stress is negative, the result is a pure pulsating compressive stress.
- If the maximum and minimum stresses act in opposite directions and are not equal, the result is an alternating stress.
${{\sigma }_{m}}=0$: This indicates a pure alternating stress.
${{\sigma }_{m}}>0:$
- If the maximum and minimum stresses act in opposite directions and are not equal, the result is an alternating stress.
- If the minimum stress equals zero and the maximum stress is positive, the result is a pure pulsating tensile stress.
- If the maximum and minimum stresses are both positive, the result is a pulsating tensile stress.
交变应力
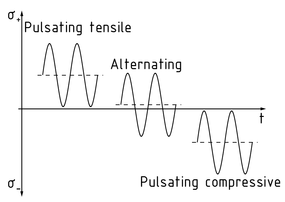
在交变应力情况下,构件上的应力随时间周期性变化,且应力的方向随时间交替变化。最大应力 ${{\sigma }_{o}}$ 与最小应力 ${{\sigma }_{u}}$ 的方向彼此相反。
最小应力与最大应力之比可以得出交变应力的循环特征 $R=\frac{{{\sigma }_{u}}}{{{\sigma }_{o}}}$ 。平均应力 ${{\sigma }_{m}}$ 是最大应力和最小应力的平均值。根据上述定义,下列不同条件下力的效果不同:
${{\sigma }_{m}}<0$ :
如果最大应力和最小应力都为负方向,则力的效果为脉动压应力。
如果最大应力等于零而最小应力为负方向,则力的效果为纯脉动压缩应力。
如果最大应力和最小应力方向相反且大小不等,则力的效果为交变应力。
${{\sigma }_{m}}=0$ :这种情况下力的效果为交变应力。
${{\sigma }_{m}}>0$ :
如果最大应力和最小应力方向相反且大小不等,则力的效果为交变应力。
如果最小应力等于零而最大应力为正方向,则力的效果为纯脉动拉伸应力。
如果最大应力和最小应力都为正方向,则力的效果为脉动拉伸应力。
交变应力/脉动应力的应力图
