
Seleccione uno
o más idiomas
0,1,3
- Alemán
- Inglés
- Chino
- Español
Extrusión (metal)
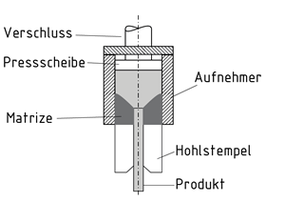
La extrusión es un proceso que se usa para producir vástagos, tubos y perfiles con metales ligeros y pesados, acero y compuestos metálicos. Se debe distinguir entre los procesos de extrusión en frío y en caliente, usados para comprimir tochos.
Durante la extrusión directa, el tocho es comprimido al diámetro del orificio contenedor y presionado a través del troquel de conformado. Los movimientos relativos entre el tocho y el contenedor requieren trabajo de fricción, el cual, cuando se comprimen tochos a través de troqueles cónicos, por ejemplo, se puede facilitar con una película de lubricante.
En la extrusión indirecta libre de fricción, el tocho es comprimido primero en el contenedor, el cual se cierra con un émbolo. El troquel es apoyado por un punzón hueco estacionario e insertado en el contenedor. Durante el proceso de extrusión, el tocho y el contenedor se mueven juntos.
En la extrusión sin una coraza, se seleccionan combinaciones de disco de presión y de contenedor para prevenir la formación de corazas en la zona exterior recortada del tocho.
Otros procesos de extrusión incluyen la extrusión hidrostática y de hydrafilm.
Extrusión directa
Strangpressen (Metall)
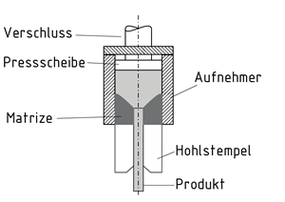
Strangpressen ist ein Verfahren zur Herstellung von Stangen, Rohren und Profilen aus Leicht- und Schwermetallen, Stahl sowie metallischen Verbundwerkstoffen. Unterschieden werden Kalt- und Warm-Strangpressverfahren zum Verpressen von Blöcken.
Beim direkten Strangpressen wird der Block auf den Durchmesser der Aufnehmer-Bohrung gestaucht und durch formgebende Matrizen gepresst. Relativbewegungen zwischen Block und Aufnehmer erfordern Reibungsarbeit, die etwa beim Pressen durch konische Matrizen mittels einen Schmierfilm erleichtert werden.
Beim reibungsfreien indirekten Strangpressen wird der Block zunächst im Aufnehmer aufgestaucht, der durch einen Stempel verschlossen wird. Die Matrize wird von einem feststehenden Hohlstempel abgestützt und in den Aufnehmer eingetaucht. Beim Pressen bewegen sich Block und Aufnehmer gemeinsam.
Beim Strangpressen ohne Schale werden Kombinationen von Pressscheibe und Aufnahme gewählt, die die Bildung von Schalen in der abgescherten Blockaußenzone vermeiden.
Hydra-Film- und hydrostatisches Verfahren sind weitere Strangpress-Verfahren.
Extrusion (metal)
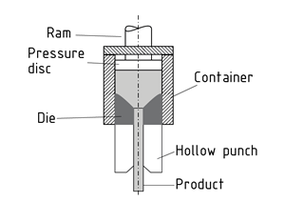
Extrusion is a process used to produce rods, tubes and profiles from light and heavy metals, Steel and metallic composites. A distinction is made between cold and hot extrusion processes used to compress billets.
During direct extrusion, the billet is compressed to the diameter of the container bore and pressed through the Forming die. Relative movements between the billet and container require friction Work, which - when compressing billets through conical dies, for example - is made easier by a film of lubricant.
In friction-free indirect extrusion, the billet is first compressed in the container, which is closed by a ram. The die is supported by a stationary hollow punch and inserted into the container. During the extrusion process, the billet and container move together.
In extrusion without a shell, pressure disc and container combinations are selected to prevent the formation of shells in the sheared-off outer zone of the billet.
Other extrusion processes include hydrafilm and hydrostatic extrusion.
挤压(金属)
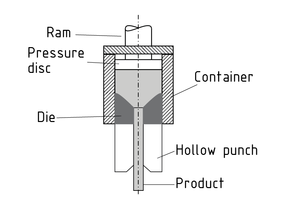
挤压是一种使用轻金属和重金属、钢和金属复合材料生产棒材,管件和型材的工艺。压缩方坯可分为冷挤法和热挤法。
直接挤压工艺中,坯段规格被压缩到容器孔的直径大小,并通过成型模加压。坯段和容器之间的相对运动需要摩擦作用 - 例如坯段被施压通过拉模时 - 使用润滑剂膜会使其更加容易。
无摩擦间接挤压时,坯段首先在容器中被压缩,由一个柱塞封闭。模具由一个固定的中空冲头支撑,并插在容器中。在挤压工艺中,坯段和容器一起移动。
无壳挤压时,选择使用压环和容器的组合,可以防止在坯段的剪切断外区结壳。
其他挤压工艺包括液压膜和静液力挤压。
直接挤压工艺
