
Seleccione uno
o más idiomas
0,1,3
- Alemán
- Inglés
- Chino
- Español
Método de Newton
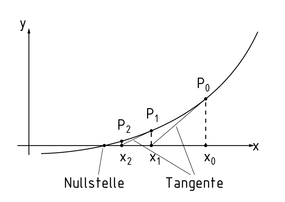
El método de Newton es un método efectivo de aproximación de ecuaciones que no pueden resolverse de manera exacta. Involucra la determinación de las raíces de funciones diferenciables y es un método de iteración.
Una aproximación ${{x}_{1}}$ se calcula desde un valor aproximado x0 para resolver la ecuación $f(x)=0$ y, a su vez, se calculan más aproximaciones ( ${{x}_{2}}$ , ${{x}_{3}}$ , etc.) para esto. Los valores deben aproximarse aún más a la solución y a ${{x}_{n+1}}={{x}_{n}}-\frac{f({{x}_{n)}}}{{{f}^{'}}({{x}_{n}})}$ .
El método de Newton se puede ilustrar geométricamente para funciones reales calculando la tangente de una función en un punto inicial y usando la raíz de la tangente como una mejor aproximación a la raíz de la función.
Ilustración geométrica del método de Newton
Newton-Verfahren
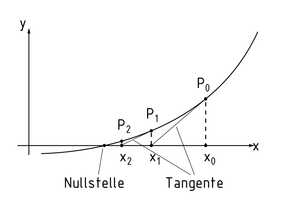
Das Newton-Verfahren ist ein Näherungsverfahren, mit dem nicht exakt lösbare Gleichungen effektiv bestimmt werden können. Dabei werden die Nullstellen einer differenzierbaren Funktion ermittelt. Das Verfahren gehört zu den Iterationsverfahren.
Aus einem Näherungswert x0 für die Lösung der Gleichung $f(x)=0$ wird eine Näherung ${{x}_{1}}$ berechnet und aus dieser wiederum weitere Näherungen ${{x}_{2}}$, ${{x}_{3}}$etc. Die Werte sollen sich dabei der Lösung immer weiter annähern. Es gilt dabei ${{x}_{n+1}}={{x}_{n}}-\frac{f({{x}_{n)}}}{{{f}^{'}}({{x}_{n}})}$.
Für reelle Funktionen ist das Newton-Verfahren geometrisch darstellbar, indem die Tangente einer Funktion in einem Ausgangspunkt errechnet wird und die Nullstelle der Tangente als verbesserte Näherung an die Nullstelle der Funktion dient.
Newton's method
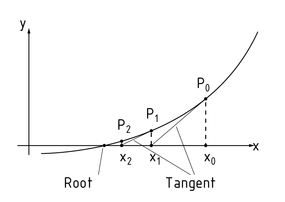
Newton's method is an effective method for approximating equations that cannot be solved exactly. It involves determining the roots of a differentiable function and is an iteration method.
An approximation ${{x}_{1}}$ is calculated from an approximate value x0 for solving the equation $f(x)=0$ and further approximations (${{x}_{2}}$, ${{x}_{3}}$, etc.) are calculated from this in turn. The values should get ever closer to the solution and ${{x}_{n+1}}={{x}_{n}}-\frac{f({{x}_{n)}}}{{{f}^{'}}({{x}_{n}})}$.
Newton's method can be illustrated geometrically for real functions by calculating the tangent of a function at an initial point and using the root of the tangent as a better approximation of the function's root.
牛顿法
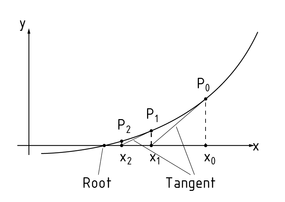
牛顿法 是一种近似求解方程的有效方法。它是一种迭代法,用于求解可微函数的根。
利用初始近似值 x0 计算方程 $f(x)=0$ 的一次近似值 ${{x}_{1}}$ ,依此类推,计算其他近似值 (${{x}_{2}}$, ${{x}_{3}}$,等等。)随着计算的不断深入,将会得到更精确的近似解,其计算公式为 ${{x}_{n+1}}={{x}_{n}}-\frac{f({{x}_{n)}}}{{{f}^{'}}({{x}_{n}})}$。
牛顿法在几何上可以解释为,计算函数在初始点处的切线,切线与x轴交点的横坐标即为方程根的近似值。
牛顿迭代法的几何解释
