
Seleccione uno
o más idiomas
0,1,3
- Alemán
- Inglés
- Chino
- Español
Centro de gravedad
El centro de gravedad de un cuerpo, el cual también es referido como el centro de masa, es un punto de representación. Si un cuerpo homogéneo es apoyado o suspendido en su centro de gravedad permanece en posición y no rota.
Las líneas de gravedad (bidimensional) y los planos de gravedad (tridimensional) se intersectan en el centro de gravedad. En el caso de un cuerpo suspendido, las líneas de gravedad apuntan desde el punto de suspensión relevante A hacia el centro del planeta.
En los casos de los cuerpos homogéneos, el centroide de volumen corresponde al centro de masa. Si un cuerpo no presenta la misma densidad en todas sus partes, es decir, si no es homogéneo, el centro de masa se ubicará en las áreas que tengan mayor densidad y, de este modo, se alejará del centroide de volumen.
Centroide de un área y centroide de una línea. El centroide de un área es el punto en que las líneas de gravedad de un área se intersectan. En el caso de una línea recta, el centroide de una línea está a la mitad de su longitud.
Centroide de área de un polígono
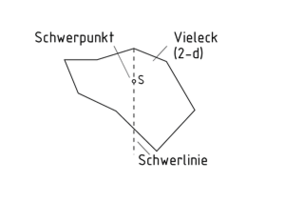
Schwerpunkt
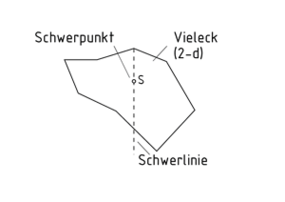
Der Schwerpunkt eines Körpers, auch als Massenmittelpunkt bezeichnet, ist ein ihn repräsentierender Punkt. Wird ein homogener Körper an seinem Schwerpunkt abgestützt oder aufgehängt, verbleibt er in seiner Lage, ohne eine Drehbewegung auszuführen.
Im Schwerpunkt Schneiden sich die jeweiligen Schwerlinien (zweidimensional) bzw. Schwerebenen (dreidimensional). Die Schwerlinien zeigen bei einem aufgehängten Körper vom jeweiligen Aufhängepunkt A in Richtung Erdmittelpunkt.
- Der Volumenschwerpunkt entspricht bei homogenen Körpern dem Massenmittelpunkt. Weist der Körper nicht an jeder Stelle die gleiche Dichte auf, ist also nicht homogen, so verschiebt sich der Massenmittelpunkt zu den Bereichen mit höherer Dichte hin und entspricht daher nicht mehr dem Volumenschwerpunkt.
- Flächen- und Linienschwerpunkt. Ein Flächenschwerpunkt ist der Schnittpunkt der Schwerlinien einer Fläche. Der Linienschwerpunkt ist bei einer geraden Linie auf halber Länge zu finden.
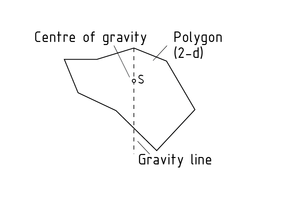
Centre of gravity
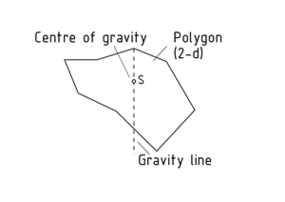
The centre of gravity of a body, which is also referred to as the centre of mass, is a representative point. If a homogeneous body is supported or suspended at its centre of gravity it stays in position and does not rotate.
The gravity lines (two dimensional) and gravity planes (three dimensional) intersect at the centre of gravity. In the case of a suspended body, gravity lines point from the relevant suspension point A towards the centre of the planet.
- In the case of homogeneous bodies, the centroid of volume corresponds to the centre of mass. If the body does not exhibit the same density throughout - i.e. if it is not homogeneous - the centre of mass will be located towards the areas that are higher in density, thereby moving it away from the centroid of volume.
- Centroid of an area and centroid of a line. The centroid of an area is the point where the gravity lines of an area intersect. In the case of a straight line, the centroid of a line is half way along its length.
重心
物体的重心是一个有代表性的质点,也被称为质心。如果一个均匀的物体在其重心位置被支撑或悬挂,那么该物体将处于原位并且不会旋转。
不同的重力线(二维)和重力面(三维)会在物体重心处相交。当物体被悬挂时,重力线从对应的悬挂点A指向物体平面的中心位置。
对于均匀物体而言,其体心对应着质心。如果物体的整体密度不均匀,即如果物体不是匀质的,质心将会偏向于密度大的一侧,从而偏离体心位置。
面心和线心。面心为面上重力线相交对应的点。对于直线而言,线心为线的中点。
多边形区域的质心
